Decoding Your Skin’s SOS: Understanding Itching, Redness, and Sweating
Experiencing persistent itching and redness? Don’t dismiss these seemingly minor skin irritations. They could be a symptom of various underlying conditions, some requiring medical attention. This comprehensive guide explores common culprits and offers practical strategies for relief.
Common Skin Irritations: Unmasking the Culprits
Itching and redness aren’t always straightforward. Let’s examine some frequent causes:
1. Contact Dermatitis: When Your Skin Reacts to its Environment

Contact dermatitis arises when your skin encounters a substance it’s sensitive to, leading to inflammation. This common type of eczema can be triggered by allergens (allergic contact dermatitis) or direct irritants (irritant contact dermatitis). Common triggers include soaps, detergents, cosmetics, jewelry (especially nickel), latex, certain fabrics, and dyes. Symptoms manifest as red, inflamed skin, itching, burning, and potentially blisters or dry patches, often confined to the contact area. Treatment involves avoiding the trigger, using fragrance-free moisturizers, and possibly over-the-counter corticosteroids (always consult a pharmacist or doctor). Persistent or severe cases demand a dermatologist’s expertise.
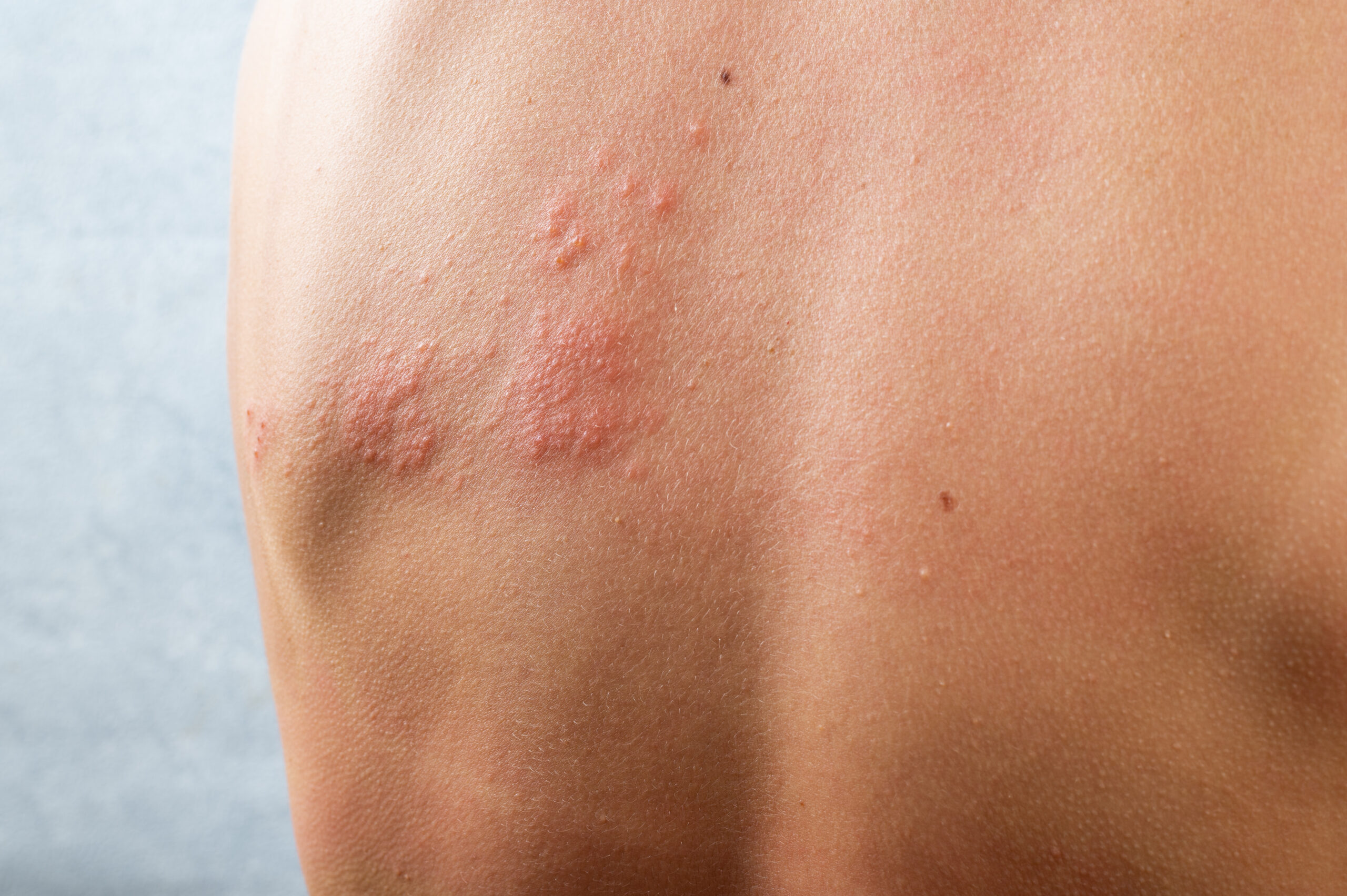
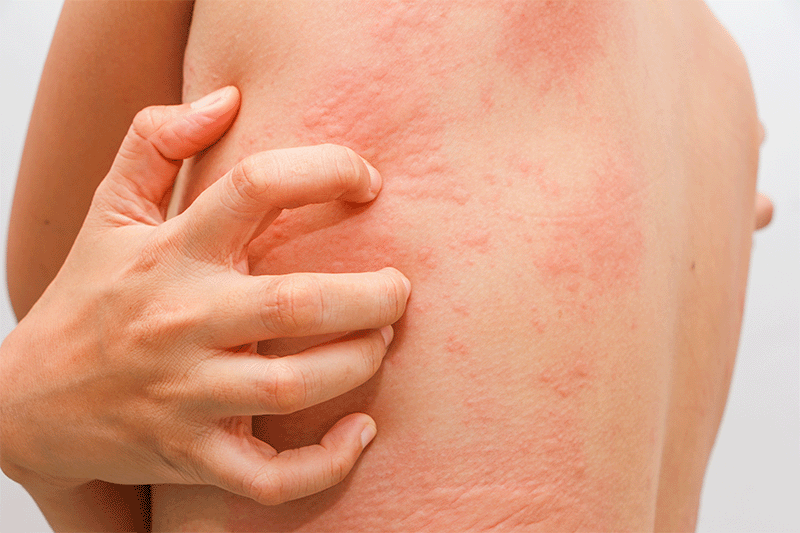
2. Heat Rash (Miliaria): The Sweat Trap
:quality(85):upscale()/2024/07/17/643/n/1922153/b734bdbd6697d4ae3bfd60.11441998_.jpg)
Heat rash occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, trapping sweat under the skin. Hot, humid conditions and intense physical activity are major contributors. Tiny red or clear bumps, a prickling or stinging sensation, and itchy skin, particularly under clothing or in skin folds (chest, back, neck, or armpits), are typical signs. Fortunately, keeping the area cool and dry, wearing loose clothing, and avoiding overheating usually resolves the issue within days.
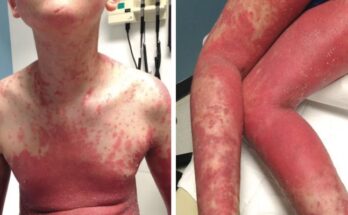
3. Allergic Reactions: Your Immune System’s Overreaction
Allergic skin reactions can stem from various sources: food, insect bites, medications, or environmental allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander). Hives (raised, itchy welts), red patches, and swelling are telltale signs. Severe reactions, including breathing or swallowing difficulties, necessitate immediate emergency care. For milder reactions, antihistamines may provide relief. The key to long-term management is identifying and avoiding the allergen.
4. Fungal Infections: Thriving in Moisture

Fungal infections like ringworm (tinea), athlete’s foot, and yeast infections flourish in warm, moist environments. Heavy sweating or wearing tight, non-breathable clothing increases the risk. Symptoms include itchy, red, circular patches with raised edges, peeling or cracked skin, and a burning or stinging sensation, often affecting the feet, groin, or underarms. Maintaining skin dryness and cleanliness, using antifungal creams or powders, and avoiding shared personal items are crucial. Stubborn or severe infections may require prescription medication.
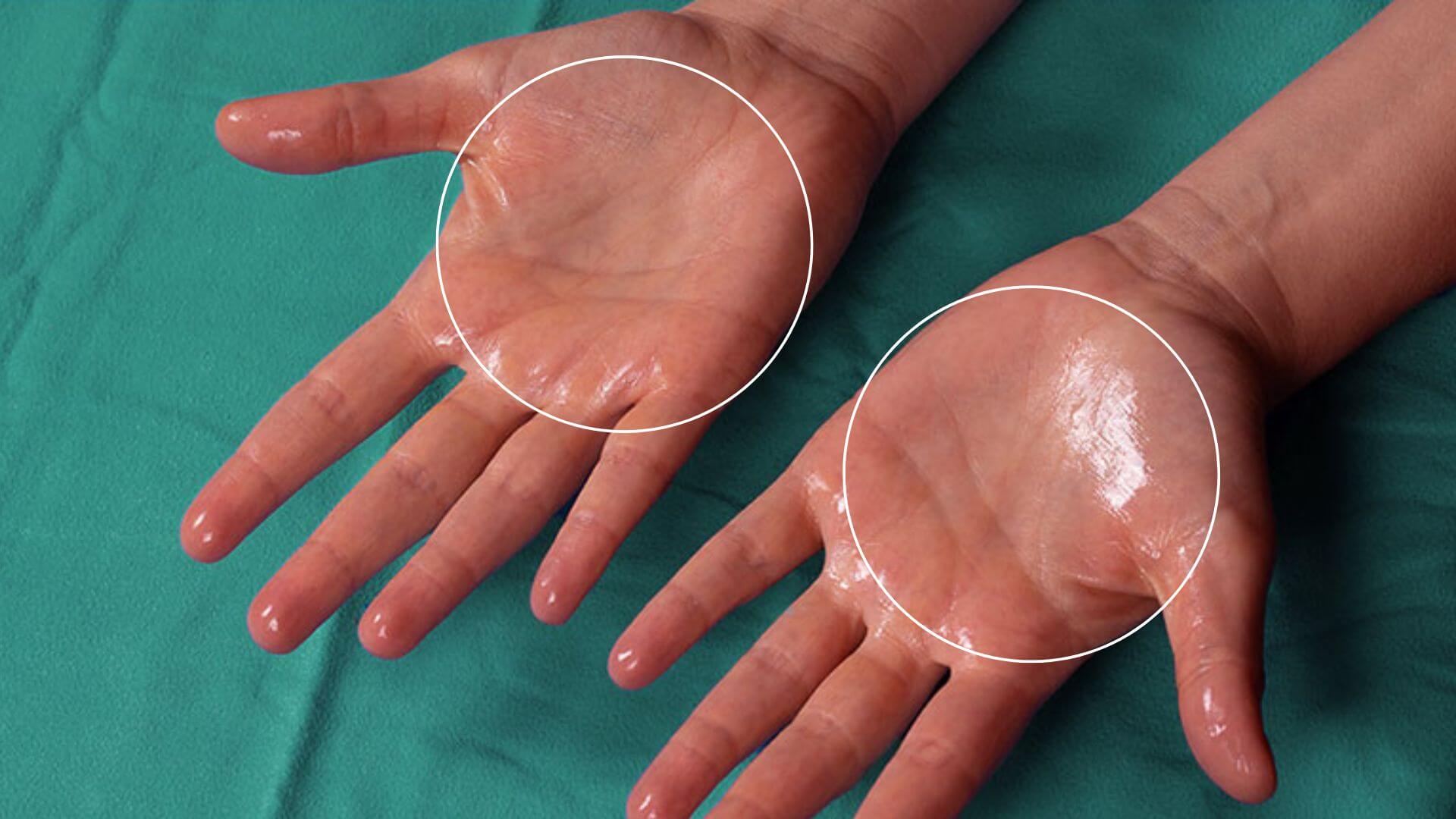
5. Hyperhidrosis: Excessive Sweating Beyond Normal

Hyperhidrosis is a condition marked by excessive sweating beyond the body’s thermoregulatory needs. It might affect specific areas (hands, feet, armpits) or be more widespread. Persistent sweating (even in cool environments), skin irritation from constant moisture, increased risk of fungal/bacterial infections, and emotional/social distress are common symptoms. Treatment options, guided by a dermatologist, range from clinical-strength antiperspirants and oral medications to Botox injections and even surgery, depending on severity.
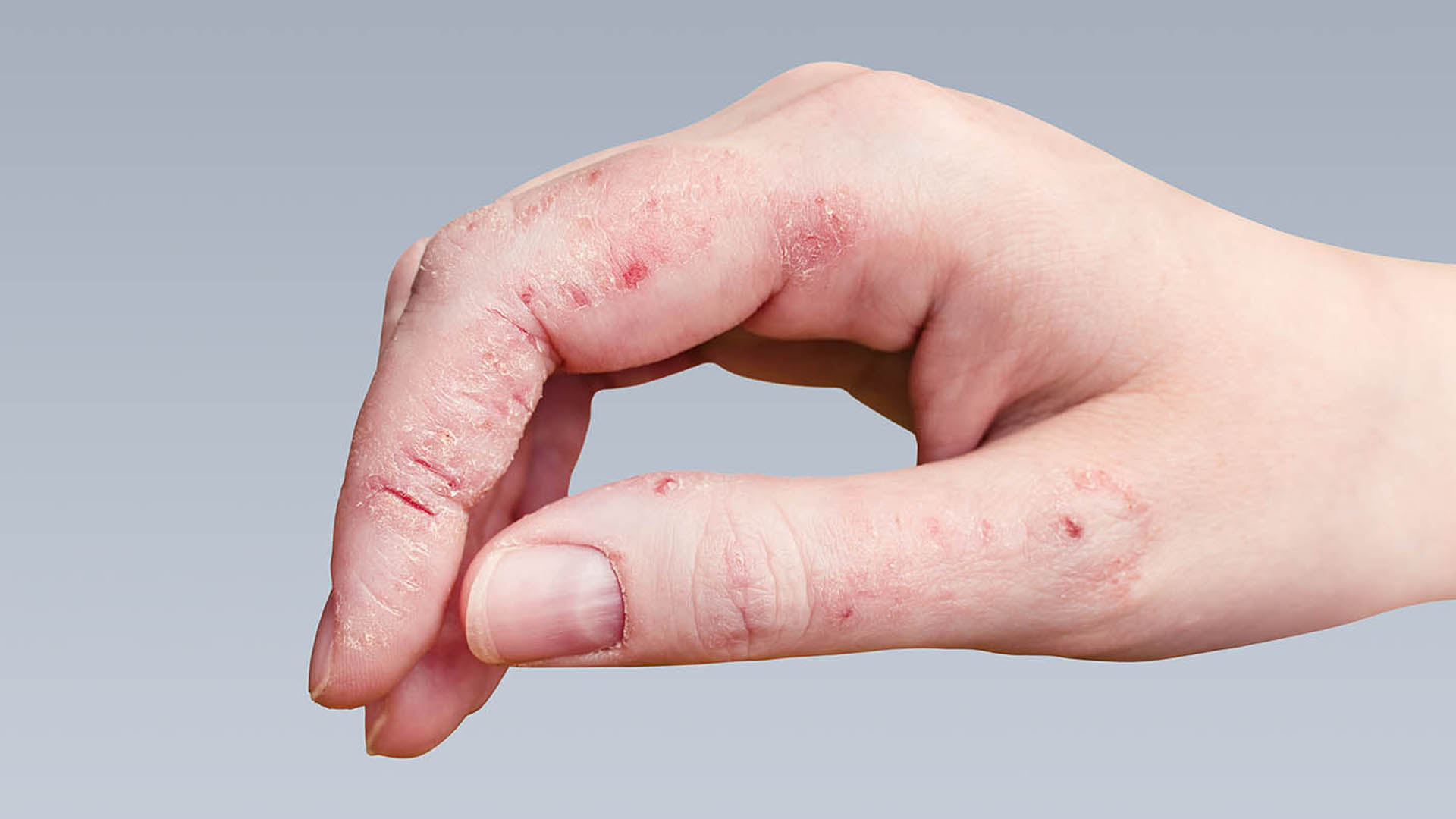
6. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Chronic Skin Inflammation
Eczema is a chronic condition causing inflamed, itchy, and dry skin. Flare-ups are common and often linked to asthma or hay fever. Red, dry, scaly patches, intense itching, and skin thickening or cracking from scratching are typical symptoms, frequently affecting elbows, knees, face, or neck. Regular moisturizing with emollient creams, avoiding triggers (allergens, stress), and using prescribed topical treatments are key to management. While not contagious, it often requires long-term care.
7. Psoriasis: Accelerated Skin Cell Growth

Psoriasis, an autoimmune disease, accelerates skin cell production, leading to rapid buildup on the skin’s surface. Thick, red patches covered with silvery-white scales, accompanied by itching or burning, often appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Treatment options include topical creams, phototherapy, and immune-modulating medications. While incurable, it’s manageable with appropriate care.
When to Seek Professional Help
While occasional itching and redness might be minor, persistent or severe symptoms warrant medical attention. Consult a doctor if symptoms last over a week, redness intensifies or spreads, open sores or infection signs (pus, swelling, fever) appear, itching disrupts sleep or daily life, or triggers remain unidentified. A dermatologist can diagnose the underlying cause through skin tests, biopsies, or bloodwork.
Home Management Strategies
While seeking professional help is vital for serious issues, you can also take proactive steps at home:
- Stay cool: Utilize fans or air conditioning, and wear loose clothing.
- Moisturize daily: Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic lotions or creams.
- Avoid irritants: Be mindful of soaps, detergents, and perfumes.
- Practice good hygiene: Shower after sweating and wear breathable fabrics.
- Track your symptoms: Maintain a diary noting foods, environments, and products to identify potential triggers.
Conclusion: Listen to Your Skin
Itching, redness, and sweating might seem insignificant, but they can signal underlying health concerns. Understanding potential causes empowers you to manage your skin health effectively and seek appropriate care when needed. Remember, your body sends signals – listen to them and consult a healthcare professional when necessary.